Overview
- EPPLUS is
- No Dependency on excel, It will even work if you don’t have excel installed on your system
- In Active development with good community support
- Open-source with good Documentation
- Duel license mode, It’s free for non-commercial use but paid for commercial use
- Requirements
- .NET Framework or .NET Core
- EPPLUS has a lot of features, I am going to focus only on reading and writing data to excel file
Setup
- Add Nuget package
EPPlus- I am using version 8.0.0 for non-commercial use
- Use version
4.5.3 if you need to use it for commercial use
- Create new excel file
sample.xlsx - For our tutorial I am going to add some data to our excel file, refer Screenshot 1
Screenshot 1 : Excel sheet with data
Read Data from Active Excel File
- Here First thing we need to specify is license type, this is only required for version 5.0.0 and above
- We also need the file path of our excel file, current file path is specific to my system, so you need to change it according to your system
- Then we need to open our excel file using
ExcelPackage class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| private static void Main()
{
//Set License for Non-Commercial Use
ExcelPackage.License.SetNonCommercialPersonal("Vivek");
var excelFilePath = @"C:\Users\Ryzen2600x\Downloads\Test.xlsx";
using (var package = new ExcelPackage(new FileInfo(excelFilePath)))
{
ExcelWorkbook wb = package.Workbook;
ExcelWorksheet ws = wb.Worksheets["Sheet1"];
// Get Cell value using row and column index
ExcelRange cell1 = ws.Cells[1, 2];
Console.WriteLine("Cell value for Row 1, column 2 = " + cell1.Value);
//Get Cell value using address
ExcelRange cell2=ws.Cells["B1"];
Console.WriteLine("B1 Cell value = " + cell2.Value);
}
}
|
Worksheet
- When you don’t want specify sheet name use sheet index
1
2
| //If you only have single Sheet
var ws = wb.Worksheets.First();
|
1
2
| //If you have multiple sheets, use sheet index
var ws = wb.Worksheets[0];
|
1
2
| //If you want to get active sheet or sheet which is last used by user
ExcelWorksheet activeSheet = wb.Worksheets.FirstOrDefault(sheet => sheet.View.TabSelected);
|
Data Range
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| ExcelRange dataRange = ws.Cells["B4:E7"];
for (int i = dataRange.Start.Row; i <= dataRange.End.Row; i++)
{
for (int j = dataRange.Start.Column; j <= dataRange.End.Column; j++)
{
ExcelRange cell = ws.Cells[i, j];
Console.WriteLine($"Value at {cell.Address}: {cell.Value}");
}
}
|
Name Range
1
2
3
| ExcelNamedRange namedRange = wb.Names["Area"];
Console.WriteLine("Area NameRange value = " + namedRange.Value);
Console.WriteLine("Area NameRange address = " + namedRange.Address);
|
Table
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| ExcelTable tbl = ws.Tables["ColumnDataTable"];
for (int i = 0; i < tbl.Address.Rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < tbl.Address.Columns; j++)
{
Console.Write(ws.Cells[tbl.Address.Start.Address].Offset(i, j).Value + ",");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
|
Write data to excel file
- Use this sample code to write data to excel file
- This code will create new excel file if file does not exist yet, if you already have file then it will overwrite it
- With EPPlus v4.5.3, writing xlsm file is not working properly when you overwrite existing file, so choose another version for this use case
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| private static void Main()
{
//Set License for Non-Commercial Use
ExcelPackage.License.SetNonCommercialPersonal("Vivek");
var excelFilePath = @"C:\Users\Ryzen2600x\Downloads\Report.xlsx";
using (var package = new ExcelPackage(excelFilePath))
{
ExcelWorksheet ws = package.Workbook.Worksheets.Add("Data");
//Add new sheet to workbook
ExcelWorksheet ws = wb.Worksheets.Add($"Sheet{wb.Worksheets.Count + 1}");
//Add some data using cell address or row and column index
ws.Cells["A1"].Value = "Hello World!";
ws.Cells[2, 1].Value = "This string is coming from CSharp";
// Save file
// Overwrite file if it already exist
package.Save();
}
}
|
Open and SaveAs File
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| using (var package = new ExcelPackage(excelFilePath))
{
ExcelWorkbook wb = package.Workbook;
ExcelWorksheet ws = wb.Worksheets.Add($"Sheet{wb.Worksheets.Count + 1}");
var cell = ws.Cells["A1"];
cell.Value = "New File";
// Save to new file
var newFilePath = @"C:\Users\Ryzen2600x\Downloads\NewReport.xlsx";
package.SaveAs(newFilePath);
}
|
Use Fix Sheet Name
1
2
3
4
5
6
| ExcelWorksheet ws = package.Workbook.Worksheets["Data"];
if (ws ==null)
{
//Add new sheet if not exists
ws = package.Workbook.Worksheets.Add("Data");
}
|
- You can also delete old sheet and then add new one if you want to start from fresh
1
2
3
4
5
| ExcelWorksheet ws = package.Workbook.Worksheets["Data"];
if (ws !=null)
{
package.Workbook.Worksheets.Delete(ws);
}
|
1
2
3
| ws.Cells["A1"].Value = "10";
ws.Cells["A2"].Value = "5";
ws.Cells["A3"].Formula = "=A1*A2";
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| ExcelRange cell = ws.Cells["A4"];
cell.Value = 0.25;
cell.Style.Font.Bold = true;
cell.Style.Font.Color.SetColor(Color.Red);
cell.Style.Fill.PatternType = OfficeOpenXml.Style.ExcelFillStyle.Solid;
cell.Style.Fill.BackgroundColor.SetColor(Color.LightYellow);
cell.Style.Border.BorderAround(OfficeOpenXml.Style.ExcelBorderStyle.Thin);
cell.Style.Numberformat.Format = "0.00%";
|
Name Range
1
2
3
| ExcelRange cell = ws.Cells["A4"];
ws.Names.Add("Area", cell);
ws.Cells["Area"].Value = 100;
|
Table
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| ExcelTable tbl = ws.Tables["ColumnDataTable"];
if (tbl is null)
{
tbl = ws.Tables.Add(ws.Cells["B11:D14"], "ColumnDataTable");
}
tbl.TableStyle = TableStyles.Medium2;
ws.Cells[tbl.Address.Start.Address].Offset(0, 0).Value = "ID";
ws.Cells[tbl.Address.Start.Address].Offset(0, 1).Value = "Length";
ws.Cells[tbl.Address.Start.Address].Offset(0, 2).Value = "Width";
for (int i = 0; i < tbl.Address.Rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < tbl.Address.Columns; j++)
{
if (i > 0)
{
ws.Cells[tbl.Address.Start.Address].Offset(i, j).Value = $"{i+1}{j+1}";
}
}
}
|
Conclusion
- EPPLUS has almost all the features that you’ll ever need to read and write excel file
- I have been using EPPlus since version 3 and it’s working great for me
- It has everything you’ll ever need to read and write excel file using C#
If you have any questions or want to discuss something : Join our comment section
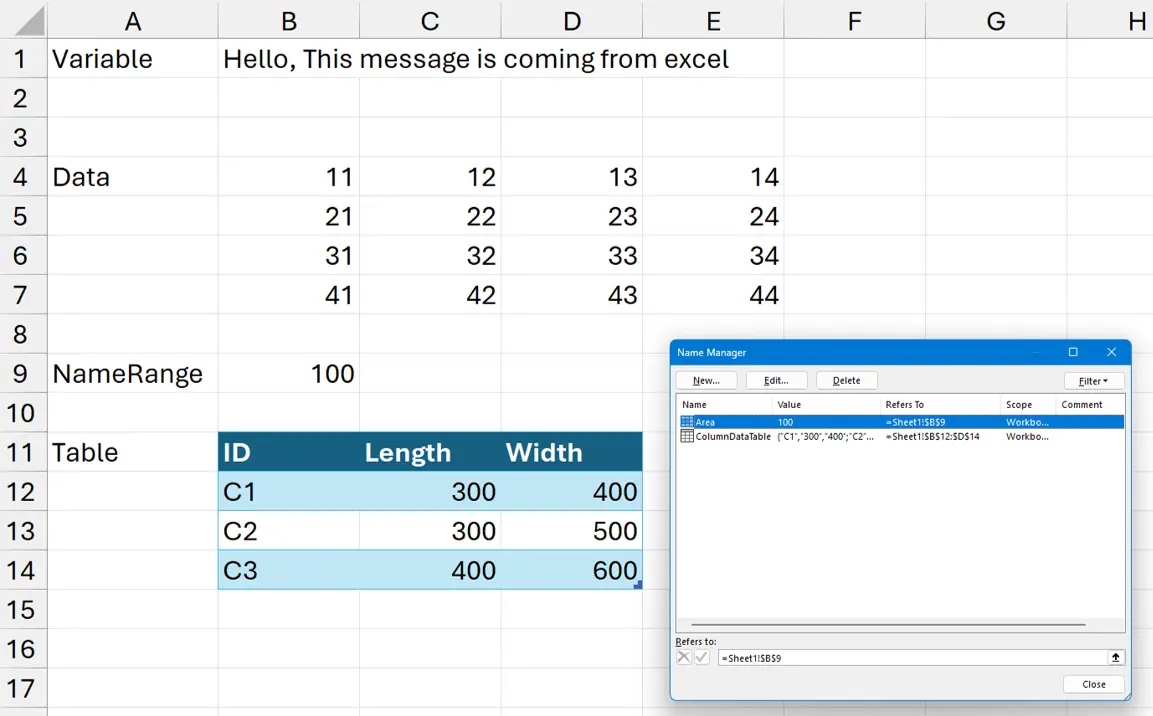 Screenshot 1 : Excel sheet with data
Screenshot 1 : Excel sheet with data