ErrorHandling
Error Handling Syntax
'Normal code with Runtime Error
Sub Test()
Dim x As Integer
x = "Test"
Debug.Print x
End Sub
'Code with Defult Error Handling
'This Code will Behave Same as Normal Code
'Go to 0 mean jump to That Line
Sub Test_Default()
On Error GoTo 0
Dim x As Integer
x = "Test"
Debug.Print x
End Sub
'If You need to Ignore Erorr
Sub Test_Ignore_Error()
On Error Resume Next
Dim x As Integer
x = "Test"
Debug.Print x
End Sub
'Code with Error Handling
Sub Test_GoTO_Handler()
On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
Dim x As Integer
x = "Test"
Debug.Print x
Done:
Exit Sub
ErrorHandler:
MsgBox (Err.Description)
End Sub
Details of Error Object
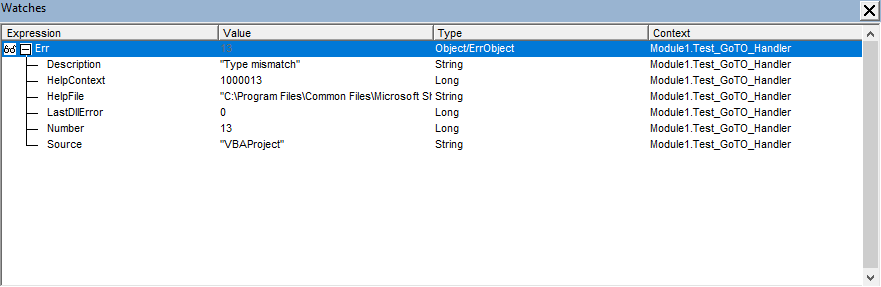
Error Handing Settings
-
Default
-
Change To Break On All Error To Debug if Error Handing code is used and Set Back to Default
Raise New Error
Err.Raise allows us to create errors. We can use it to create custom errors for our application which is very useful. It is the equivalent of the Throw statement in Java\C#.
The format is as follows
When we create an error using Err.Raise we need to give it a number. We can use any number from 513 to 65535 for our error. We must use vbObjectError with the number e.g.Public Const ERROR_INVALID_DATA As Long = vbObjectError + 513
'Raise New Erorr
Sub Test_Raise_Error()
On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
Dim x As Integer
x = 6
If x >= 5 Then
Err.Raise ERROR_INVALID_DATA, "Test_Raise_Error", "The value Must Be less than 5"
End If
Done:
Exit Sub
ErrorHandler:
MsgBox (Err.Description)
End Sub